How Does a Twin-Screw Extruder Work? -2
2. Material Conveyance
Working components: screw, barrel
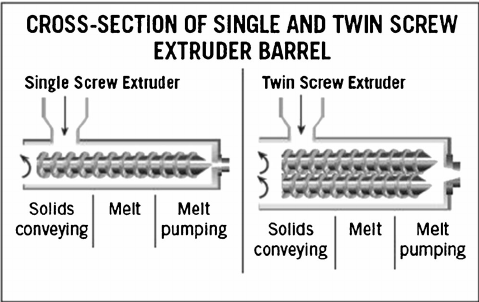
After the material enters the extruder barrel, it is conveyed along the barrel axial direction by the rotating screw. The conveying stage is mainly to convey the material from the feed port to the compression zone and start heating.
Non-meshing twin-screw extruders cannot form a closed or semi-closed cavity, and there is no positive displacement conveying condition. The material conveying mechanism is similar to that of a single-screw extruder.
Meshing twin-screw extruders mainly convey materials by forced conveying (positive displacement conveying). Different models of twin-screw extruders have different positive displacement conveying capabilities and slight differences in conveying mechanisms. The degree of positive displacement depends on the proximity of the flight of one screw to the relative flight of the other screw. Counter-rotating extruders with tightly interlocked screw configurations produce a significant level of positive displacement conveying characteristics.
3. Compression Stage
Plastic gradually starts to melt from a solid state in the compression section while being compressed. In this section, the plastic is subjected to the effects of compression ratio and barrel heating + friction heat, the material temperature rises quickly, the friction effect inside the material is large, and the compression effect is large.
4. Melting Stage
When the material enters the melting section, it gradually heats up and begins to melt under the action of the barrel heater. At this stage, the screw continues to rotate, further compressing and advancing the molten material. The rotation of the screw not only provides propulsion, but also makes the material evenly distributed in the screw groove through the design of the thread, thereby ensuring the quality and stability of the molten material.
5. Mixing Stage
Working components: twin screws, mixing elements
The mixing stage includes distributive mixing and dispersive mixing, which ensures that the components are evenly distributed and aggregates are eliminated through the shearing action of the screw.
In addition, twin screw extruders excel at mixing components through the interlocking action of the screws, generating turbulence and shear forces. This results in an efficient mixing process as the material undergoes collision and compression. Whether it involves coordinating polymers, dispersing additives, or integrating fillers, parallel co-rotating twin screw extruders always achieve precise and consistent results.
6. Exhaust Stage
Due to the hungry feeding, a large lead screw conveying element can be used to make the screw groove in an unfilled state and in a zero pressure state, so that the exhaust section can be set. In order to ensure product quality, the gas and volatiles in the melt need to be discharged at this stage. The exhaust zone is usually equipped with a vacuum port to effectively remove the gas and volatiles in the melt.
(To be continued...)





