How Does a Twin-Screw Extruder Work? -1
The twin screw extruder has traditionally been used to produce pellets so that the material can be continuously fed into secondary processing equipment, such as injection molding machines or single-screw extruders.
In addition, twin-screw extruders can also produce films, fibers, sheets pipes, profiles..., which is called direct extrusion. The two forms of products are obtained through basically the same production steps.
Based on this, this article mainly introduces how twin-screw extruders work so that you can understand the production of products.
Demand for Plastic Compounding and Pelletizing:
Twin screw extruders are mainly used for compounding and pelletizing of some plastic products:
Flame-retardant plastics: PA6, PA66, PET, PBT, PP, PC and other materials are improved in flame retardancy by adding flame retardants
Highly filled plastics: PE and PP are filled with 75% CaCO3 to enhance rigidity and stability
Insulating plastics: Different additives (such as flame retardants, antioxidants, etc.) are evenly dispersed in the matrix resin to ensure the uniformity and stability of insulating plastics
Thermoplastic plastics: BPAT materials are compounded with materials such as PLA and EPS to have good toughness, ductility and high temperature resistance.
Thermosensitive materials: C-PVC products are added with heat stabilizers and lubricants to facilitate subsequent extrusion molding. The functionality of the material is ensured through precise temperature control
Degradable materials: PLA and PBAT, ESR and other degradable materials are modified to improve their elongation and other problems
How Does a Twin-Screw Extruder Work?
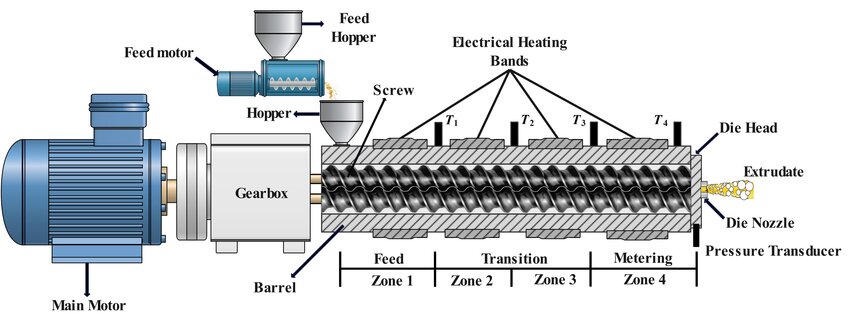
1. Material Intake
Working components: feed hopper, feed throat
In a twin-screw extruder, the hopper plays a vital role in conveying solid materials to the feed zone of the extruder. Specifically, the hopper pushes the solid material into the extruder through the feeding hole at the bottom of the hopper where it connects to the barrel. This process is usually accompanied by a cooling jacket to ensure the stability of the material flow and prevent overheating.
In the feed zone, the solid material is pushed forward by the rotation of the screw and gradually melted due to the screw gap and the friction between the screw and the barrel. This melting mechanism is different from the conductive melting and dispersion melting in the single-screw extruder, and the melting mechanism of the twin-screw extruder is completely different.
In addition, the side feeder can also be used to push the solid material into the molten polymer in the extruder. The side feeder consists of a hopper and a set of conveying screws, which are designed to push the solid material into the feed zone of the extruder and connect the side feeder to the vacuum port of the air trapped in the solid through a combined barrel, thereby reducing the entrained air.
(To be continued....)





