Influence of main indexes of chlorinated polyethylene (CPE) on modification of rigid PVC(2)
Effect of different volatile CPE on PVC modification:
CPE manufacturers generally use aqueous phase (acid phase) suspension chlorination process, in the chlorination reaction process, some hydrogen atoms in polyethylene molecules are replaced by chlorine atoms, resulting in chlorinated polyethylene and hydrogen chloride.
Since the production of CPE is carried out in suspension and hydrogen chloride is produced during this process, the volatiles in CPE products contain both water and hydrogen chloride gas that evaporates from inside CPE molecules at high temperatures. Hydrogen chloride has a catalytic effect on the decomposition of CPE, especially PVC, which will greatly accelerate the decomposition and dehydrochlorination reaction, and aggravate the degradation of PVC macromolecules and the cross-linking of broken chain molecules, thus affecting the processing and mechanical properties of PVC products.
Practice has shown that the volatile fraction of CPE products has a great impact on the physical properties and processing properties of CPE and PVC blends, so the volatile fraction of CPE is a very important technical quality index of chlorinated polyethylene.
The production process of CPE mainly includes chlorination reaction, plate filtration, centrifugal dehydration, drying, grinding, coating and packaging. The different conditions of centrifugal dehydration and drying process will lead to differences in the volatiles of CPE produced.
According to the results of CPE dehydrochlorination experiment, it is found that the higher the volatile content of CPE, the shorter the time needed to remove a certain concentration of hydrogen chloride, and the worse the stability. This is because the higher the volatile content of CPE, the more volatiles it contains, such as water and hydrogen chloride gas, and hydrogen chloride also plays a catalytic role in the decomposition of CPE, speeding up the decomposition and dehydrogenation of CPE.
Rheological experiments showed that the higher the CPE volatile content, the shorter the plasticization time of PVC/CPE composite, and the faster the plasticization. With the increase of CPE volatiles, the plasticization time decreased and the plasticization increased. The maximum and minimum torques also tend to increase. The balance torque of the composite modified by the selected CPE sample is basically the same, which may be related to the same raw material and the same molecular weight of HDPE
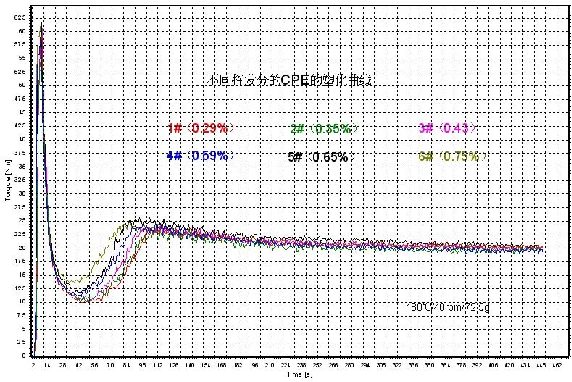
Through the detection of notch impact strength, welding strength and profile surface color difference of PVC/CPE composites with different volatile fractions added, it can be found that with the increase of CPE volatile fractions, the physical and mechanical properties of PVC/CPE composites prepared with different volatile fractions show a downward trend. The single V notch impact strength of the composite modified with 0.43% CPE sample has been reduced to only 20.2 KJ/m2 at room temperature.
With the increase of CPE volatile content, the color difference (b value) of composite material profiles gradually increases, and yellowing phenomenon appears on the surface of profiles. When the volatile content of CPE reaches 0.75%, the color difference of profiles is larger, the surface yellowing is serious, and the inner bar and inner wall have foaming phenomenon, which may be due to the large volatile content of CPE, resulting in more hydrogen chloride extraction and poor stability. And the reasons for too fast plasticization.
However, the composite modified by CPE sample with a welding strength of 0.59% volatile content is still higher, possibly because although the plasticization is fast, the high plasticization is beneficial to the welding strength, until the welding strength of the composite modified by CPE sample with a volatile content of 0.65% is significantly reduced.
The plasticizing time and physical and mechanical properties of PVC/CPE composites are affected by different volatile CPE. With the increase of volatile fraction, the plasticizing time of the composite decreases, the plasticizing speed increases, and the mixing block turns yellow gradually.
The physical and mechanical properties of the composites decreased with the increase of volatile content. The higher the volatile content of CPE, the shorter the time it takes to remove a certain concentration of hydrogen chloride, and the worse the stability, this law is consistent with the plasticization speed of PVC/CPE composite. CPE with chlorine content of about 36% and volatile content ≤0.43% is more suitable as an impact modifier for PVC. Volatiles as a measure of CPE performance index for PVC plastic processing is of practical guiding significance.





