Processing technology of chlorinated polyvinyl chloride (PVC-C) pipes - 1
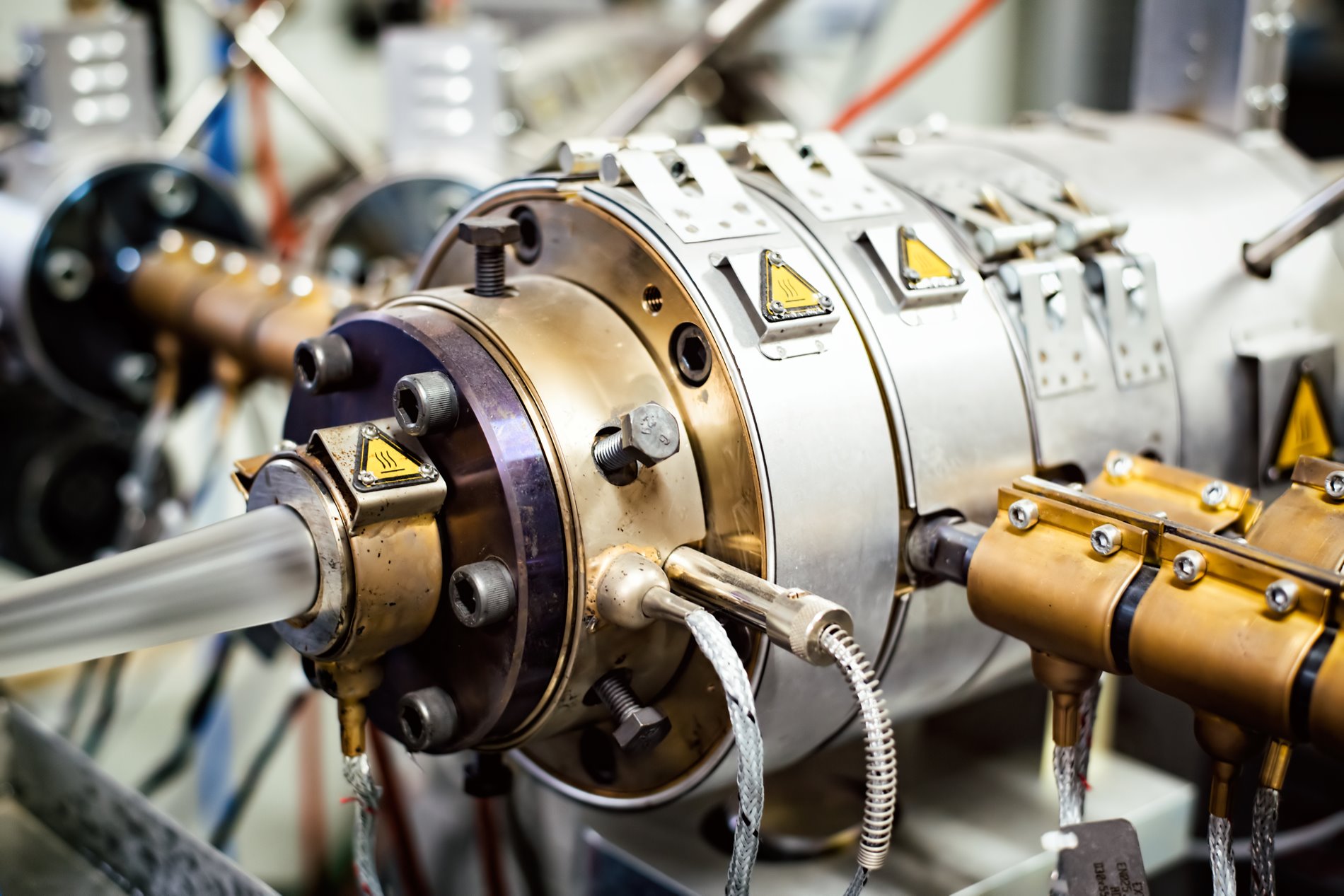
1. Extruder
Extrusion processing of CPVC pipes usually uses parallel or conical twin-screw extruders.
In view of the fact that CPVC is easier to plasticize than PVC, it is easier to control the extrusion production of CPVC pipes by using a parallel twin-screw extruder. If lead salt stabilizer is used in the formula, the extruder must have good plasticizing performance; if organotin is used in the formula as stabilizer, the compression ratio of the extruder screw must not be too large.
2. Processing technology
2.1 Mixing of materials
The mixing process of CPVC resin is the same as that of PVC resin.
It requires two processes:
High-speed mixing and low-speed cooling mixing.
Generally, the high-speed mixing temperature should be controlled at 110 to 120°C, not too high, otherwise it is easy to mix yellowing materials and cause problems during the extrusion process.
The decomposition of materials or the phenomenon of "over-plasticization" may occur.
The temperature of low-speed cooling and mixing is controlled at 40 to 50°C, and cannot be too high.
Otherwise, the mixed material will be too different from the room temperature, causing the material to absorb too much moisture in the air and affecting the performance of the product.
2.2 Extrusion temperature
The extrusion process of CPVC pipes focuses on the process temperature, which will directly affect the plasticization quality of the pipes.
Generally, the process temperature will vary greatly depending on the plasticizing performance of the extruder, and sometimes the difference will be 20 to 30°C.
Theoretically, when using a special CPVC extruder to produce CPVC pipes, the processing temperature of CPVC materials is higher than that of PVC.
In actual operation, when using a PVC extruder to produce CPVC pipes, the processing temperature of CPVC may be lower than that of PVC. The processing temperature of CPVC is sometimes 5 to 8°C lower, especially when using a PVC extruder for producing highly filled PVC products. This is because the melt viscosity of CPVC is larger than that of PVC, and a large amount of friction heat will be generated between the molten molecules. At this time, if the extruder provides too much heat to it, it will easily cause the material to decompose.
(To be continued...)





